Units of the International System
The International System (abbreviated SI, for Systeme International, the French name for the system) was adopted in 1960 by the 11th General Conference on Weights and Measures. An expanded and modified version of the metric system, International System addresses the needs of modern science for additional and more accurate units of measurement. The key features of the International System are decimalization, a system of prefixes, and a standard defined in terms of an invariable physical measure.Base Units
The International System has base units from which all others in the system are derived. The standards for the base units, except for the kilogram, are defined by unchanging and reproducible physical occurences. For example, the meter is defined as the distance traveled by light in a vacuum in 1/299,792,458 of a second. The standard for the kilogram is a platinum-iridium cylinder kept at the International Bureau of Weights and Standards in Sèvres, France.| Unit | Quantity | Symbol |
|---|---|---|
| meter | length | m |
| kilogram | mass | kg |
| second | time | s |
| ampere | electric current | A |
| kelvin | temperature | K |
| mole | amount of matter | mol |
| candela | luminous intensity | cd |
Supplementary Units
The International System uses two supplementary units that are based on abstract geometrical concepts rather than physical standards.| Unit | Quantity | Symbol |
|---|---|---|
| radian | plane angles | rad |
| steradian | solid angles | sr |
Prefixes
A multiple of a unit in the International System is formed by adding a prefix to the name of that unit. The prefixes change the magnitude of the unit by orders of ten from 1024 to 10-24.| Prefix | Symbol | Multiplying Factor |
|---|---|---|
| yotta- | Y | 1024 = 1,000,000,000,000,000,000,000,000 |
| zetta- | Z | 1021 = 1,000,000,000,000,000,000,000 |
| exa- | E | 1018 = 1,000,000,000,000,000,000 |
| peta- | P | 1015 = 1,000,000,000,000,000 |
| tera- | T | 1012 = 1,000,000,000,000 |
| giga- | G | 109 = 1,000,000,000 |
| mega- | M | 106 = 1,000,000 |
| kilo- | K | 103 = 1,000 |
| hecto- | h | 102 = 1000 |
| deca- | da | 10 = 10 |
| deci- | d | 10-1 = 0.1 |
| centi- | c | 10-2 = 0.01 |
| milli- | m | 10-3 = 0.001 |
| micro- | 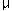 |
10-6 = 0.000,001 |
| nano- | n | 10-9 = 0.000,000,001 |
| pico- | p | 10-12 = 0.000,000,000,001 |
| femto- | f | 10-15 = 0.000,000,000,000,001 |
| atto- | a | 10-18 = 0.000,000,000,000,000,001 |
| zepto- | z | 10-21 = 0.000,000,000,000,000,000,001 |
| yocto- | y | 10-24 = 0.000,000,000,000,000,000,000,001 |
Additional Units
Listed below are a few of the non-SI units that are commonly used with the International System.| Unit | Quantity | Symbol |
|---|---|---|
| angstrom (= 10-10m) | length | Å |
| electron-volt (= 0.160 aJ) | energy | eV |
| hectare (= 10,000 m2) | land area | ha |
| liter (= 1.0dm3) | volume or capacity | l |
| standard atmosphere (= 101.3 kPa) | pressure | atm |
Derived Units
Most of the units in the International System are derived units, that is units defined in terms of base units and supplementary units. Derived units can be divided into two groups - those that have a special name and symbol, and those that do not.| Without Names and Symbols | |
|---|---|
| Measure of | Derivation |
| acceleration | m/s2 |
| angular acceleration | rad/s2 |
| angular velocity | rad/s |
| density | kg/m3 |
| electric field strength | V/m |
| luminance | cd/m2 |
| magnetic field strength | A/m |
| velocity | m/s |
| With Names and Symbols | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Unit | Measure of | Symbol | Derivation |
| coulomb | electric charge | C | A·s |
| farad | electric capacitance | F | A·s/V |
| henry | inductance | H | V·s/A |
| hertz | frequency | Hz | cycles/s |
| joule | quantity of energy | J | N·m |
| lumen | flux of light | lm | cd·sr |
| lux | illumination | lx | lm/m2 |
| newton | force | N | kg·m/s2 |
| ohm | electric resistance | 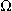 |
V/A |
| pascal | pressure | Pa | N/m2 |
| tesla | magnetic flux density | T | Wb/m2 |
| volt | voltage | V | W/A |
| watt | power | W | J/s |
| weber | magnetic flux | Wb | V·s |